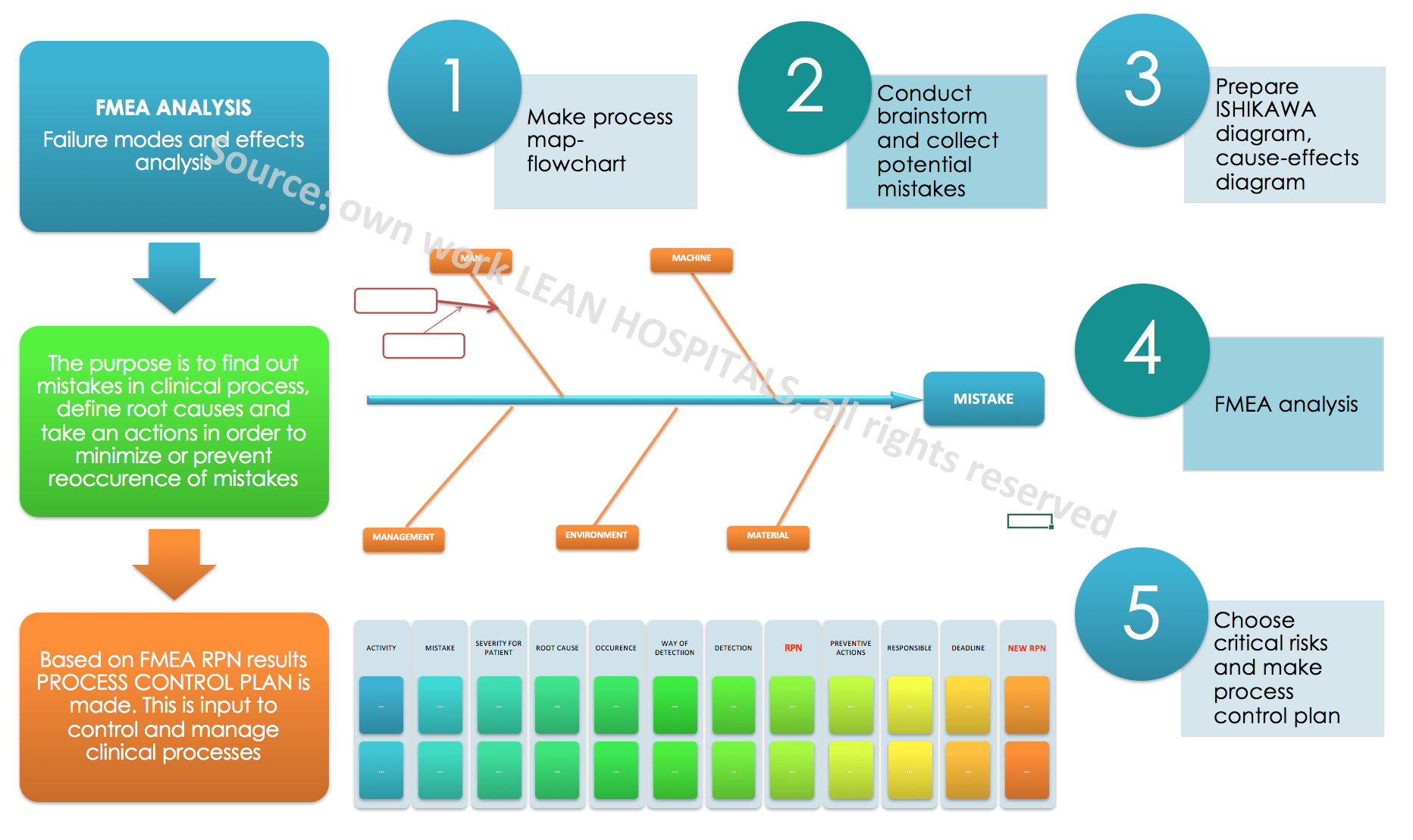
FMEA analysis in hospital
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) in hospital
Every day while working in a hospital, a doctor’s office or laboratory there may occur situations that can cause errors and generate costs. Sometimes these are necessary activities related to the provision of a medical service, sometimes these are activities that could be avoided. These activities may be related to mistakes and errors that are not detected at an early stage of creation can bring huge losses to the organization. Not only financial but also reputational losses. Analyzing the operating costs of medical institution, they can be divided into fixed and variable costs.
Fixed costs usually remain at a comparable level, while variable costs depend not only on the number of patients who use the hospital services each year but also on the number and complexity of processes, i.e. services offered by the medical institution. Each hospital ward, clinic, laboratory consists of main and auxiliary processes. Each process consists of activities in which there are potential risks. Each risk is a potential cost for the company and additional work.
Risk management
Failure mode and effects analysis FMEA is not only an additional way to solve problems but also a way to meet the new requirements of the Quality Management System according to ISO 9001: 2015. Risk management is a set of activities that are aimed at controlling the risk. Clinical risk is the combination of the probability of an event and its consequences, which will have a negative impact on the outcome of the patient treatment. There are many methods of risk management and what will be chosen depends not only on the decisions of main management but also on:
- The number of processes occurring in the organization
- Complexity of processes and level of maturity
- Employees awareness of processes
- Accessibility of resources, i.e.: working time of medical and non-medical personnel, available conference room
- Employees knowledge of risk analysis
The methods of risk estimation, most often used, are presented below:
- FMEA method- failure mode and effects analysis- The FMEA analysis is divided into:
- SFMEA- FMEA for the management system
- PFMEA- FMEA for the clinical process
- DFMEA- FMEA for design, construction of medical equipment
- MFMEA- FMEA for machinery, medical equipment
- SAC analysis
- Strategic management
The goals of using the FMEA in a medical institution:
- Identification of the causes of errors
- Documenting the process
- Permanent elimination of errors in the process and critical places / activities that may be a “weak link”
- Continuous improvement of the process through the introduction of amendments and new solutions depending on the level of risk
- Creating a knowledge base on the most important processes in the organization and activities related to them, such as preventive, corrective and improving actions
A detailed analysis should be made to estimate the risk. The following stages are presented below:
- Collect the applicable procedures and instructions in the process.
- These can be procedures such as hospitalization in a ward.
- Gather process participants – create a team for risk analysis.
2.2. The team should be multidisciplinary, consisting of several different specialists related to the process as well as people who don’t work directly in the process. The team should consist of 3 to 5 people, with specializations such as doctor, nurse, technician, ward nurse or registrant. An analysis leader should be selected that will document risk estimation and organize meetings.
- Create a flowchart – a graphical diagram which shows the course of the process from the moment of requesting the service until the patient leaves the medical institution.
3.3. If such flowcharts do not exist, they can be created with the team, specifying the decision-making places, people responsible for performing the activities and the necessary medical documentation needed to perform the service. The diagram will be the basis for the analysis of individual activities. The more extensive it is, the longer the analysis will take, while it will be more detailed and the later plan will be more likely.
- Collect a register of non-conformities, adverse events, medical incidents and other if they exist.
- Collect a register of comments from patients and other interested parties.
- Collect the results of the satisfaction surveys of patients, employees and other interested parties.
- Analyze each activity for potential errors that may occur during its implementation. It is best to brainstorm for potential mistakes and collect historical data from the registers.
FMEA analysis is different from the others because it is very detailed and work-intensive. It depends on the team how the process will be analyzed and whether all information will be taken into account. The analysis should be objective and true. The analysis determines three factors on the basis of which the product is calculated which shows the level of risk. These are:
- The significance of the error for the patient
- Frequency of the defect
- The method of detecting the defect
The rating scale is from 1 to 10, with 1 being the least negative impact while 10 means the highest negative impact. The scale is universal and is used throughout the world by various industries.
- Next stage is to define the significance of the defect for the patient / client.
- The next stage is to determine the cause of the error – potential risk. There can be many reasons for any potential error. To collect them and sort thematically, dedicated tools can be used.
Only after collecting information about the process, knowing the sequence of individual activities and critical places in the process, which are particularly important and influence the result of the process, it is possible to undertake the analysis of potential risks. Potential causes of errors can be collected by usage of tools such as:
- 5WHY
- ISHIKAWA diagram – fishbone
- brainstorm (1×1, 6x3x5, 6×6 Philips)
- Knowing the potential causes of errors, the frequency of occurrence should be assessed. Participants should be asked how often the error may occur or occurred in the past. Is it once a day, a week, a year? Maybe the medical institution has statistics on recurring adverse events or other errors?
- Next stage is to specify how to detect the error. To what extent the process participants are able to notice an error during their daily work. If it is instant, using sensors and light and sound signals it’s good. If it is not possible to detect the error, this must also be included in the analysis. The methods of process supervision and error detection include such solutions as poka-yoke, jidoka, system Andon, visual management. You can find more information in lean Techniques.
- The next stage is to assess the detection of errors.
- With a specific risk factor, it is possible to calculate the RPN (Risk Priority Number). The rating range is from 1 to 1000. The higher the number, the higher the probability of risk.
The result of the RPN indicates for which risks improvement and prevention actions should be taken and which can be accepted without taking major measures. The universal scale indicates that for risks above 100 points, actions should always be taken. Such a risk is defined as critical and is probably a threat to the participants of the process, the indicated errors can be expected in the near future. The risk in the 60-100 range is high and taking action depends on the organization and decisions of not only the team but also the main management. Actions may be implemented but not mandatory. For risks below 60 points it is not needed to take action, as it is usually an acceptable level of risk. You can find more about risk management in the next article.
- Risk estimation and the RPN result is not the last stage in the analysis. The result indicates for which activities the actions should be taken. It should be remembered that the significance of the error for the patient can’t be reduced, it is possible to implement actions reducing the level of error or its detection. It all depends on the organization’s capabilities, resources, the maturity of the process and the involvement of co-workers.
- After defining the preventive actions , plan of action should be defined, which indicates how to reduce the frequency of errors and how to detect them. The action plan consists of a task, a responsible person and a deadline for implementation.
- After the action is performed, the error and the method of detection should be estimated again. The new RPN score should be lower than the original one. This will be evidence of effective actions and good risk management in clinical processes.
How to maintain the implemented changes and reduce the level of potential risks? The PCP-PROCESS CONTROL PLAN, which is created on the basis of the FMEA analysis will help us.. The plan allows for continuous monitoring of the process and the implementation of any post-audit actions. Remember that every change in the process carries with it new, potential risks that can change the action plan. For each time the order of action in the process changes, new medical equipment arrive, the place of health care implementation changes, the FMEA analysis should be reviewed and updated.
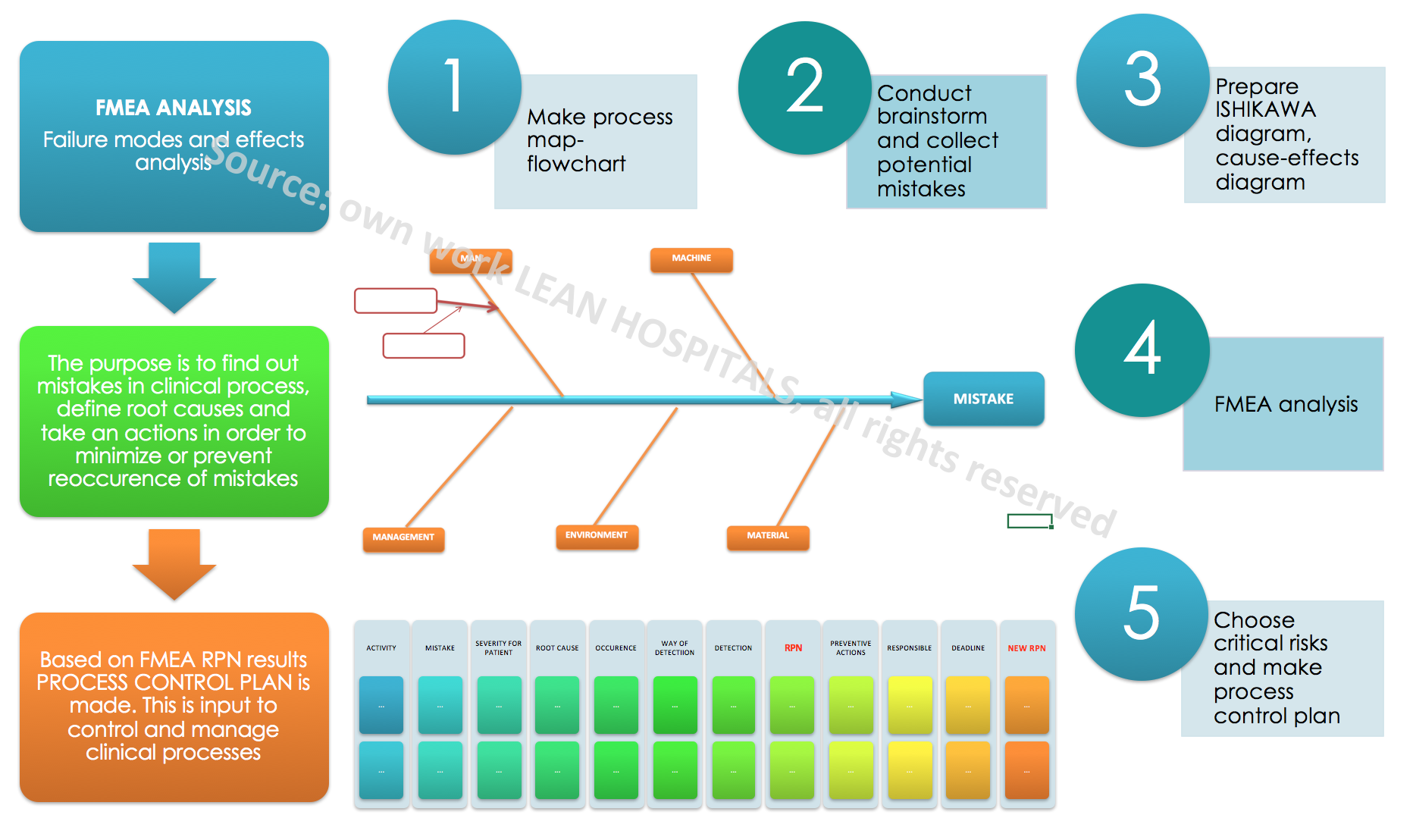
It should be remembered that without having many detailed data on risk, it isn’t possible to assess but only to estimate its level. Estimation is related to the opinion of a multidisciplinary team, which is able to determine the potential risk based on their own experience. Advantages of the method:
- Detailed knowledge of clinical processes
- Increased awareness of employees, in particular medical personnel, about the causes of errors
- Increased process cycle efficiency – PCE
- Improved patient safety
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Improved communication in the hospital because of teamwork
- Reduced costs of organization activities
Disadvantages of the method:
- The need for knowledge of extended tool
- The procedure is time-consuming
Practical experience shows that a well-made FMEA analysis allows to implement processes without any errors or mistakes. Such a positive result is achieved due to the consequences of the action and compliance with the procedures. The system created by everyone, both employees and customers.
